Record History
(Right‑click Record History pane.)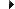
Always Record History
Update Children
Lock Children
History Break Warning
Record History
(Right‑click Record History pane.)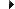
Always Record History
Update Children
Lock Children
History Break Warning
The History command stores the connection between a command's input geometry and the result so that when the input geometry changes, the result updates accordingly.
For example, with History recording and Update turned on, a lofted surface can be changed by editing the input curves.
Steps
| 1. | In the status bar, click the Record History pane. |
| 2. | Use a history-enabled command such as the Loft command to make a surface from input curves. |
| 3. | Edit the input curves. The surface updates. |
Command-line options
Controls the default Record History setting.
In general, it is best to leave the Record option set to No and use the Record History status bar pane to selectively record history. Recording history uses computer resources and makes saved files larger.
Allows output to automatically update when input is edited. This may be slow or may interfere with your workflow.
If the option is set to No, use the HistoryUpdate command to manually update the objects.
Locks child objects created with History to discourage direct geometry editing of the child object. Editing the child object directly will break the history link to the parent object.
Note: History locked objects are selectable to use as input and edit properties, but not change geometry. If full locking is needed, children can be selected and locked with Lock command.
BrokenHistoryWarning=Yes/No
Displays a warning dialog when an action is taken that breaks the link between the output and input objects. To get back, use the Undo command.
Cautions
The connection between the input objects and the output object is easily broken. The basic rules for preserving history are:
| ● | Do not purge the history from the child (output) surfaces. |
| ● | Do not delete the parent geometry (input objects - curves, surfaces, etc.) that was used to create the child surface. |
| ● | Do not control-point edit or move the child surface. |
| ● | Do not move parents and children together. |
| ● | Joining objects breaks history on the objects. |
| ● | History stored in previous versions of Rhino will not carry over to a later version. |
Overriding History Options
The status bar Record History pane reflects the current state of history recording. Click the pane to toggle the global setting for the duration of one command. If the text in the pane is bold, then recording is active, if it is not bold, recording is not active.
Change the option using the History command. This command can be run inside another command. It can also be included in a macro. This setting does not quit after one command. It must be explicitly changed.
History can be recorded without the output geometry being updated when inputs are edited.
Command prefixes for turning history on and off
Type these shortcut symbols before a command name to enable/disable history recording
# (hash)
Enables history recording.
For example: #ArcBlend
% (percent)
Disables history recording.
For example: %ArcBlend
Commands with history enabled
Commands with the following notation pay attention to history recording.
These commands can make use of history recording.
The HistoryUpdate command redefines the object based on editing its parents.
Steps
Select the objects.
Command-line options
Updates all objects.
The HistoryPurge command removes history from an object and its children.
History records can add to the file size so purging unneeded history may a good idea at times.
Warning: HistoryPurge cannot be undone.
Steps
Select the objects.
See also
Rhinoceros 5 © 2010-2015 Robert McNeel & Associates. 17-Sep-2015