BooleanUnion
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
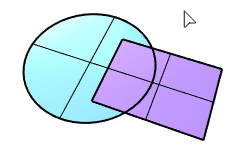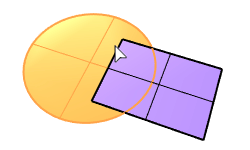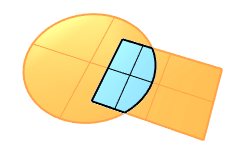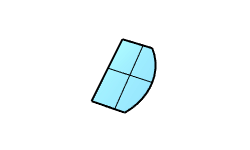
Solid Union |
The BooleanUnion command trims the shared areas of selected polysurfaces or surfaces and creates a single polysurface from the unshared areas.
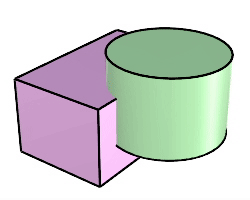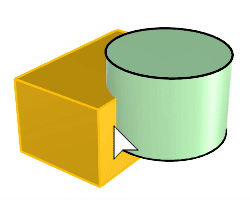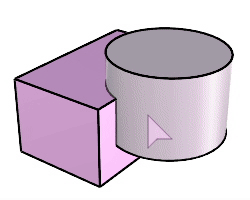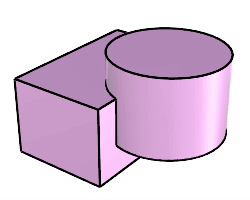
Command-line options
DeleteInput
Controls whether the original geometry is deleted.
DeleteInput=No supports History recording.
MergeCoplanarFaces
Combines adjacent coplanar faces into a single face when the Boolean operation is completed.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Solid Difference |
The BooleanDifference command trims the shared areas of selected polysurfaces or surfaces with another set of polysurfaces or surfaces.
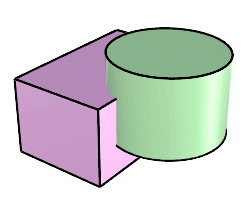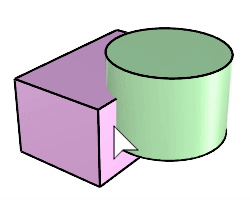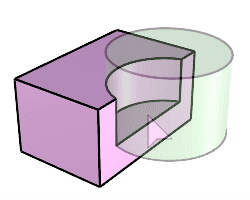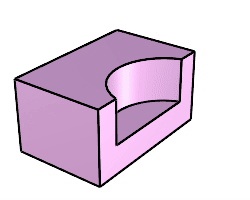
Steps
Command-line options
DeleteInput
Controls whether the original geometry is deleted.
DeleteInput=No supports History recording.
DeleteCutters
When DeleteInput=Yes, deletes the object used to subtract the other object.
- Rhino is a surface modeler. It's not possible to subtract a sphere inside another sphere to create a tennis ball-like object that has a solid wall enclosing a void.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Solid Intersection |
The BooleanIntersection command trims the unshared areas of selected polysurfaces or surfaces.
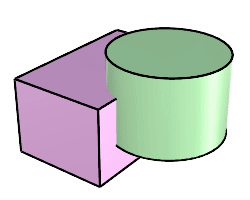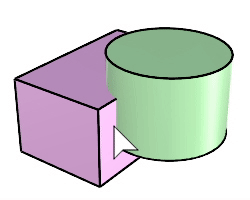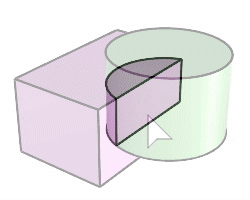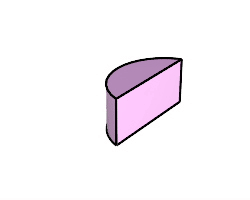
Steps
DeleteInput
Controls whether the original geometry is deleted.
DeleteInput=No supports History recording.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Solid Boolean Split |
The BooleanSplit command splits shared areas of selected polysurfaces or surfaces and creates separate polysurfaces from the shared and unshared parts.
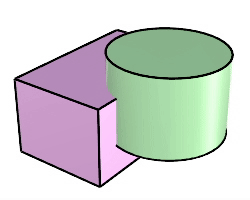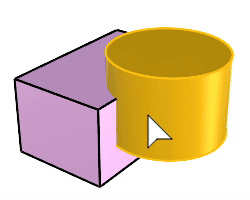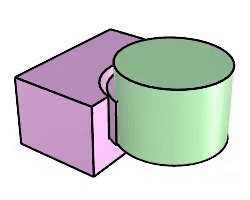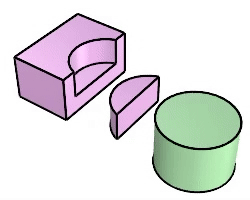
Steps
Command-line options
DeleteInput
Controls whether the original geometry is deleted.
DeleteInput=No supports History recording.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Solid Boolean Two Objects |
The Boolean2Objects command cycles through possible Boolean operations between two objects with mouse clicks.
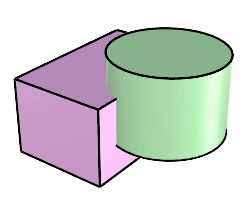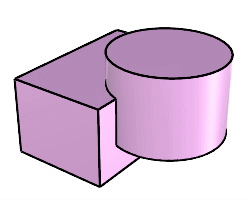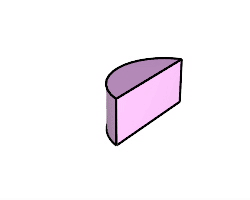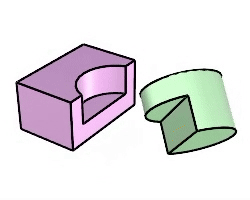
Steps
-
Select two objects.
-
Click the mouse in the viewport until you get the object you want.
Union
Difference A - B
Difference B - A
Intersection
Inverse intersection
Command-line options
DeleteInput
Controls whether the original geometry is deleted.
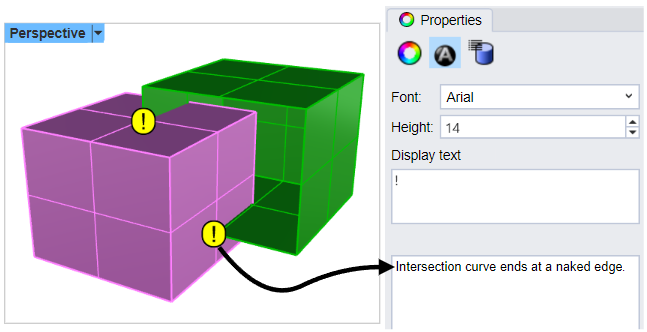
Troubleshoot Boolean Operations
If the Boolean operation fails, text dots that indicate the area where there is a naked edge or a bad intersection are placed in the model. Search for these dots to examine the area causing the problem.
Detailed information about the error is contained in the dot properties under Secondary text.
Boolean commands can be used with surfaces and open polysurfaces. The result depends on the direction of the normals of the object. Use the Dir command to see the direction. If the results are the opposite of what you want, reverse the direction of the surface with the Dir or Flip commands and try again.
Try the Join command first on surfaces.
For mesh objects the steps are the same as for the NURBS Boolean equivalent. The result of a command is always a mesh regardless of the input object type.
What makes Boolean operations fail?
Boolean operations can fail for a number of reasons:
- Normals may not point the way you expect.
- Control points tend to stack up at the intersection of the two objects.
- Objects may have overlapping surface areas.
Surface Normals
The Boolean operations use the surface normal to determine which parts to keep and which to throw away. When you attempt a BooleanDifference and you get a BooleanUnion instead, or vice versa, this is because the objects have normals that are the opposite of what you expect. This tends to happen often if one or more objects are not fully closed. If an object is not closed, Rhino has no way to determine which side is outside and which is inside. Use the Dir command to see which way the normals point on these objects and use the Flip option as needed to make sure the normal direction is what you consider to be the outside of the object. Fully closed objects will always have normals pointing outward.
Coincident Control Points
Coincident control points occur when the control points at the edge of a surface are at an identical location. For example, the tip of a cone or an untrimmed surface with three edges, or the pole of a sphere. You can also move control points to the same location. This point is also called a singularity.
When a singularity point occurs at the intersection of two objects you want to Boolean, the operation can fail.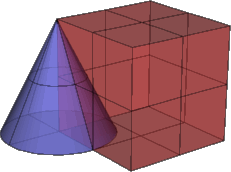
Overlapping Surface Area
Overlapping surface areas occur when two surfaces share the same area. In this example, the two boxes are just touching along one side. The objects will Union, but Difference, and Intersection will not work.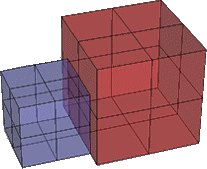
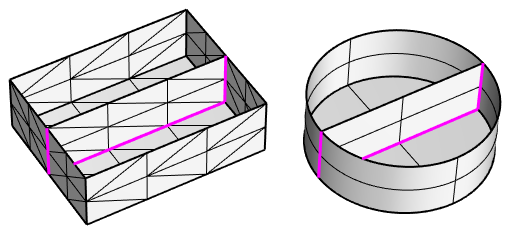
Nonmanifold edges
In addition to overlapping surfaces, non-manifold edges can also cause failures.
Edges of polysurfaces or meshes that have more than two faces joined to a single edge are non-manifold.
What to do
If your objects won't Boolean, you can use other techniques to get the results you want.
In this example, the apex of the cone is exactly at the corner of the box. This is one of the situations that can cause the Boolean operations to fail.
Instead of using Boolean operations in this case, use the Explode command to separate polysurfaces into single surfaces if necessary. Use the Intersect command to create curves that represent the intersection of the two surfaces. To create the parts, use these curves to Trim and/or Split and then Join them back together.
|
Toolbar |
Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Surface Planar Boolean |
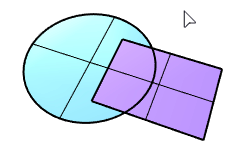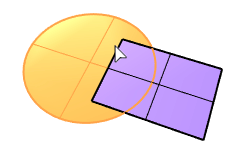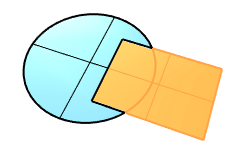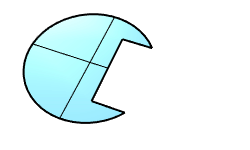
The PlanarUnion command merges overlapped planar surfaces into a single surface.
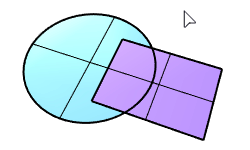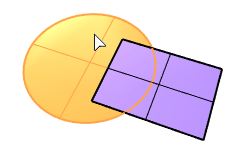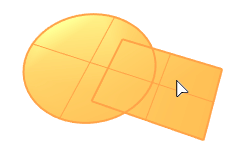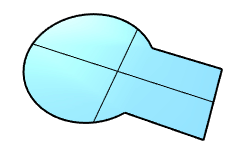
|
Toolbar |
Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Surface Planar Boolean |
The PlanarDifference command selects two overlapped planar surfaces and creates a surface from the first surface with the overlapped area trimmed off.
|
Toolbar |
Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Surface Planar Boolean |
The PlanarIntersection command creates a surface from the overlapped area of two planar surfaces.