Layout
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
View and Layout Title Layout > New Layout |
The Layout command creates a print layout viewport.
A layout viewport represents the sheet of paper that will be sent to a printer or a file such as PDF. Layouts can include various views of the model and annotations like title blocks and notes.
Two types of viewports provide different functions: model viewports and layout viewports.
In model viewports, create your surface or solid model using the appropriate units and precision.
In layout viewports, place one or more details of your model and add information that annotates the printed sheet, such as manufacturing notes, bill of materials, general notes, title blocks, seals, and scale bars.
These viewports are accessible on the tabs at the bottom of the modeling area. The ViewportTabs command turns the tabs on and off.
Detail viewports
Layout viewports contain detail viewports that...
-
display different views of the model.
-
have viewport properties that can be accessed when a detail is made active.
-
have object properties that can be accessed when a detail is selected.
The color, width... of the detail viewport edge including No Print are set in object properties.
-
are created on the current layer.
-
can only be rectangular. To define your own shape...
New Layout
Name
The layout viewport name.
See: Naming conventions in Rhino
Select Printer
Printer
Select the target printer from the list of configured printers.
Size
Select a supported paper size from the list.
Portrait / Landscape
Sets the orientation.
Width / Height
Sets the size of the paper as well as the width (x length) and height (y length) of the layout. If the paper size is not supported by the selected printer, the Printer setting will be disabled.
<inches / millimeters / centimeters>
Units for the paper size. If the selected unit is different from Document Layout Unit, the selected unit will be converted.
Initial Detail Count
The number of details to start with.
Steps
- In the New Layout dialog box, specify options.
- Draw a border or insert a title block onto the layout.
Add text that does not relate to the model such as the project name, sheet number, sheet content, and the like.
- Add annotation objects such as text and title blocks.
- Create details and arrange them on the layout.
- In each detail set up view of the model, orientation, and scale.
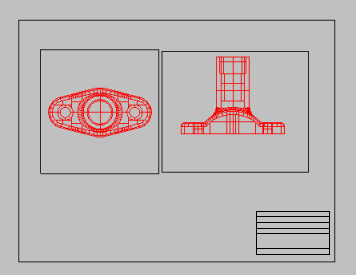
- In the layout viewport, add text and dimensions.
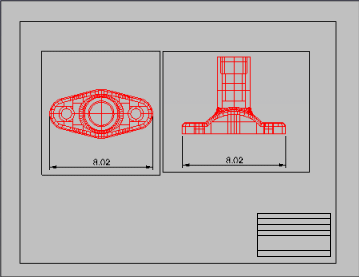
- Set the visibility of the detail edge on the printed page.
Use Properties to access the Print WidthNo Print property.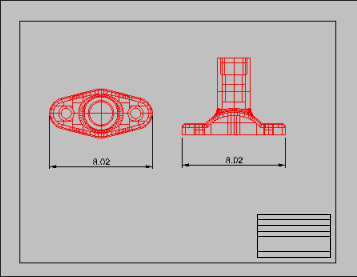
- Print.
Make layout details of any shape
You can make details of any shape using a solid white hatch in the layout.
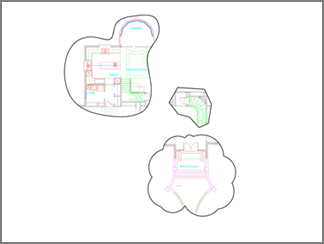
Steps
- Set up a layout with one or more details.
- Scale the details as you wish.
- In the layout, draw a rectangle from the corners of the page.
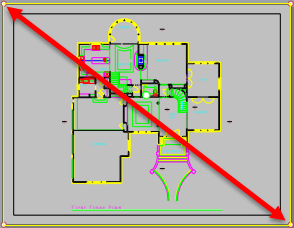
- In the layout, draw your detail shape.
Use any planar curve: Circle, Curve, InterpCrv, RevCloud, Rectangle, etc.
For accuracy, you can draw the curve in model space and then use the ChangeSpace command to move it to the layout.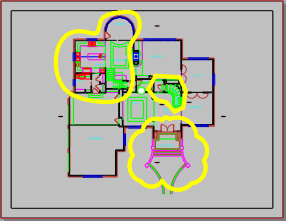
- Create a solid hatch using the rectangle at the drawing edge and the detail shapes.
- Make the color of the hatch white.
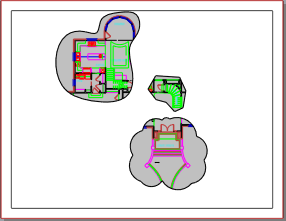
- Add anything else you want in the layout such as detail names.
- Print.
Note
- Try turning History on, then make a hatch. If you stretch the boundaries, the hatch will update.
- Use Draw Order to keep your text, title blocks, dimensions on top. It can be frustrating if the text or dims that you are looking for has gone behind the hatch.
- You cannot bring a detail above the hatch. Hatch has draw order priority to be on top.
Dimensioning distance in Layouts
In Layout viewports, objects in detail views are annotated with the model space distance.
In this example, the blue circle is in the layout viewport. Its radius is annotated as 10 units (the layout space distance). The red circle is in a detail viewport. Its radius is annotated as 100 units (the model space distance) whether the radius dimension is created in the detail viewport or the layout viewport.
Related commands
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The ChangeSpace command moves or copies objects between layout and detail viewports. This command only works in layout viewports that at least have a detail view.
To move an object from model space to layout space
- In a detail view, select the objects you want to change space.
The objects are moved to the layout page.
To move an object from layout space to model space
- Select the objects in layout space.
- Select the target detail view by clicking on the detail edge.
Note: Do not double-click the detail view.
| Command-line option | |
|---|---|
|
Copy |
Specifies whether or not the objects are copied. The RememberCopyOptions command determines whether the selected option is used as the default. |
| Toolbar | Menu | Shortcut |
|---|---|---|
|
|
File > Import From File > Layouts From 3dm File View Layout > Import |
|
The ImportLayout command imports one or more layouts from a Rhino file into the current Rhino model.
This allows defining standard title block pages in a single file and importing those pages into other Rhino files.
When multiple layouts exist, right-click to check one and clear all the others.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The CopyLayout command copies the active layout to a new layout.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The LayoutProperties command opens the Layout Properties dialog box.
Name
The layout viewport name.
See: Naming conventions in Rhino
Select Printer
Printer
Select the target printer from the list of configured printers.
Size
Select a supported paper size from the list.
Portrait / Landscape
Sets the orientation.
Width / Height
Sets the size of the paper as well as the width (x length) and height (y length) of the layout. If the paper size is not supported by the selected printer, the Printer setting will be disabled.
<inches / millimeters / centimeters>
Units for the paper size. If the selected unit is different from Document Layout Unit, the selected unit will be converted.
