Squish 指令将展开时必定会有误差 (两个方向都有曲率) 的 3D 网格或 NURBS 曲面展开为平面。
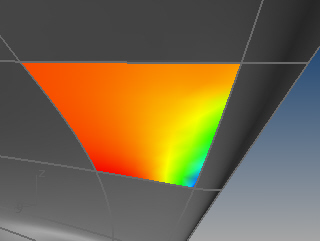
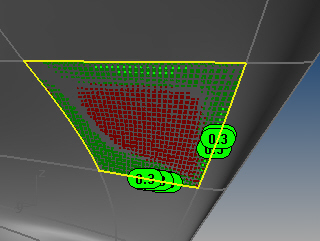
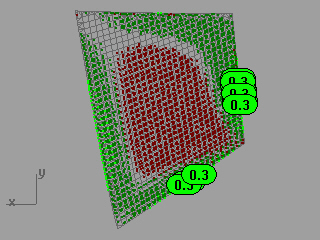
Squish 指令会将展开的平面对应回原物件时收缩的区域以红色的点云标示,延展的区域以绿色的点云标示,并在收缩与延展最明显的位置以注解点标注变形量,最多可以标注十个边缘,注解点的数字是长度增加、减少的百分比。
报告
面积
展开前后的面积差异。
收缩
将二维图案变换到三维以后材质将被压缩。展开的平面对应回原来的物件时收缩的百分比为估算值。
延展
将二维图案变换到三维以后材质将被延展。展开的平面对应回原来的物件时延展的百分比为估算值。
指令行选项
分割接缝
展开封闭的曲面 (例如:圆柱曲面) 时从接缝切开。
维持边界
尽量维持边界的长度不变。
变形
设定收缩、延展的偏好,也可以自订变形的设定。
不设限
不偏好收缩或延展。
延展为主
当展开的平面对应回原来的 3D 物件时偏好延展。
只延展
当展开的平面对应回原来的 3D 物件时偏好延展。
收缩为主
当展开的平面对应回原来的 3D 物件时偏好收缩。
只收缩
当展开的平面对应回原来的 3D 物件时只收缩不延展。
自订A/自订B/自订C
自订变形设定。
自订 选项有四个变形的参数可以设定。
边界延展
边界收缩
内部延展
内部收缩
这里的四个参数的设定预设都是 1,允许设为任何正数值。这四个参数是变形的偏好权重,例如您想尽量避免内部延展时可以像这样设定:
边界延展=1
边界收缩=1
内部延展=1
InteriorCompress=100
如果您想尽量维持边界的长度可以像这样设定:
边界延展=10
边界收缩=10
内部延展=1
内部收缩=1
自订设定
用来设定 A、B、C 三组常用的设定。
材质
设定实际制造时使用的材质类型。
硬性
Minimizes stresses when forming the 3-D surface from the 2-D pattern when a rigid material will be used for manufacture.
软性
Limits geometric distortion as much as possible when a pliable material will be used for manufacture.
外侧
向上
3D 曲面展开为 2D 平面时法线方向朝上。
向下
3D 曲面展开为 2D 平面时法线方向朝下。
标示
在展开前后的物件上以红色与绿色的点云及注解点标注变形比例。
Limitations
| ● | 不可设定剥离线 (类似剥离香蕉皮的效果)。 |
| ● | 比较不适用于可展开的曲面,可展开的曲面请使用 UnRollSrf 指令。 |
Squish is an algorithm that works on meshes. Squish flattens the mesh by "minimizing the changes in facet area and changes in facet edge lengths" between the 3‑D mesh and the 2‑D mesh, subject to some constraints.
For example, if A,B,C are the corners of a 3‑D triangle and a,b,c are the corresponding corners of the 2‑D triangle, the changes in edge length are
d1 = |Distance(A,B) - Distance(a,b)|
d2 = |Distance(B,C) - Distance(b,c)|
d3 = |DIstance(C,A) - Distance(c,a)|
da = |Area(A,B,C) - area(a,b,c)|
DL = d1+d2+d3
DL2 = d12 + d22 + d32
DA = da
DA2 = da2
D = some combination of DL, DL2, DA and DA2
The "minimizing the changes in area and or edge lengths" above means create the 2‑D mesh so that "D" is as small as possible.
In practice, there are thousands of facets and many ways to minimize D, most of which don't make practical sense. So Squish constrains the answer to prevent the 2‑D mesh from folding back onto itself and forcing certain 3‑D points end up in specified 2‑D locations.
A trimmed NURBS surface is squished by squishing a dense mesh of the surface.
The squish options determine how DA, DA2, D1 and D2 are combined and allow for more complicated ways to calculate of DA, DA2, D1, and D2 and to allow for a bias towards stretching or compression.
However, the Squish algorithm is much too simple to even begin to model the true physical properties of most materials that come in sheets, particularly those that where material thickness plays a role and those that can compress or stretch any appreciable amount,
In short, if a sheet of material is expensive, cutting it is expensive, or bending it is expensive, or related issues in the manufacturing process are time critical or money critical, then consider using Squish to give you an initial hint about the shape of a pattern, but real material and manufacturing expertise will have to be used to create a pattern that will work on the shop floor.
SquishBack 指令将展开的平面上的曲线或点物件对应至原来的 3D 曲面。
步骤
| 1. | 选取展开的曲面。 |
| 2. | Select curves and points on the pattern. |
范例
For example, suppose we wanted to put a “Rhino” brand name in the black circle on this 3-D NURBS model of a shoe last.
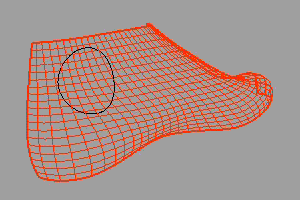
先以 Squish 指令将鞋子的曲面与其上的曲线展开为平面。
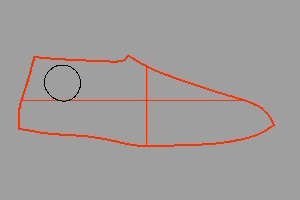
以 TextObject 指令在平面上的圆形曲线内建立“Rhino”的文字曲线。

最后再使用 SquishBack 指令将文字曲线反向对应至鞋子的 3D 曲面上。

SquishInfo 指令显示展开的平面在展开时使用的设定。
请参考
Flatten a surface without restriction to single-directional curvature.
Flatten (develop) a surface or polysurface with curvature in one direction to a planar surface.