Flow
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Transform Flow along Curve |
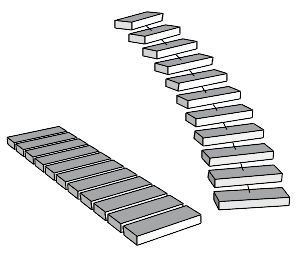
The Flow command re-aligns an object or group of objects from a base curve to a target curve.
Use the Flow command to map a flat, straight shape to a curved shape, since it can be easier to draw things when they are lined up than to draw a complex shape around a curve.
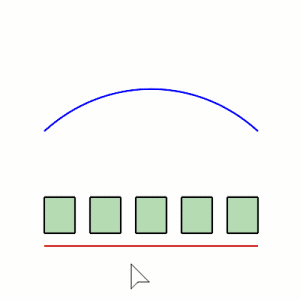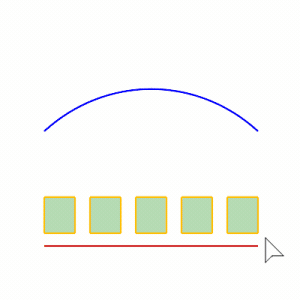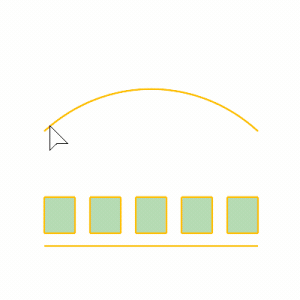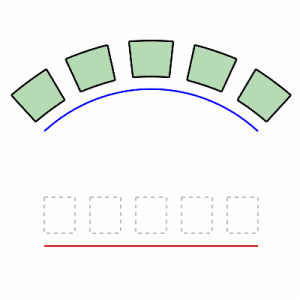
Steps
- Select objects.
- Select the base curve near one end.
- Select the target curve near the matching end.
Command-line options
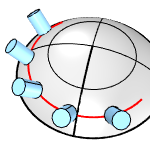
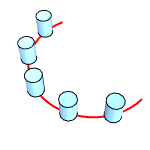
TargetSurface (For target curve only)
Uses a surface to orient objects. The "up" direction of the objects will be mapped to the surface normal.
|
|
|
|
With (left) and without (right) a target surface.
|
|
Copy
Specifies whether or not the objects are copied. A plus sign ![]() appears at the cursor when copy mode is on. The RememberCopyOptions command determines whether the selected option is used as the default.
appears at the cursor when copy mode is on. The RememberCopyOptions command determines whether the selected option is used as the default.
Rigid
Decides if objects are only relocated, but not deformed, along the target curve.
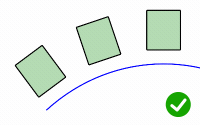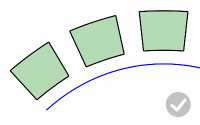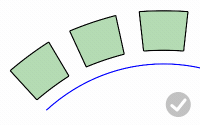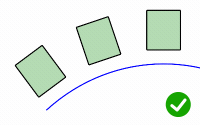
RigidGroups
Decides if the Rigid option pays attention to groups. Only available when Rigid=Yes.
Line
Draw a line to be used as the base curve.
Local
Specify circles to define a "tube" of influence around the input curve. Everything inside the tube flows. Everything outside the tube is fixed. Inside the tube wall the flow dies off.
Stretch
Decides to stretch or compress objects in the curve direction so that the relationship to the target curve is the same as it is to the base curve.
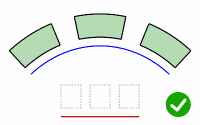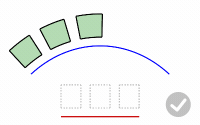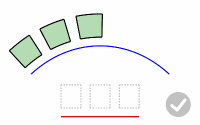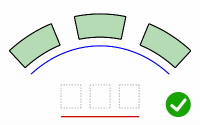
PreserveStructure
Specifies whether the knot structure of a curve or surface will be maintained after the deformation.
The PreserveStructure option does not apply to polysurfaces, and will not be displayed if polysurfaces are selected for editing.
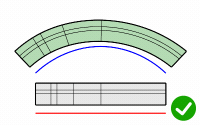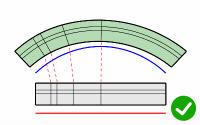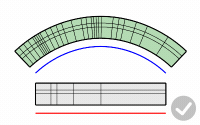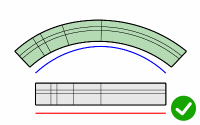
Roadlike
Uses frames (x, y, z axes) to calculate 3-D rotation when objects flow to a 3-D target curve.
Steps
-
Pick the roadlike axis base point and direction on the base curve.
-
Pick the roadlike axis base point and direction on the target curve.
- When picking the direction, press Enter, or select Automatic, to use the CPlane-Z axis.
Stairlike
This option is available when Roadlike=Yes. The objects only rotate around their z axis when flowing to the target curve.