 Texture Mapping
Texture Mapping
|
Toolbar |
Menu |
Shortcut |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Edit Object Properties Window Panels > Properties |
F3 |
Texture mapping properties manage texture map projections for selected surfaces, polysurfaces, and meshes.
Mapping is a process of defining how to represent a 2‑D image on a 3‑D model. Mapping transforms a 2‑D source image into an image buffer called a texture.
A texture can be applied to the surface of a 3‑D model to add color, texture, or other surface detail like glossiness, reflectivity, or transparency.
The problem of how to represent the texture in 3-D rendering can be overcome by means of uv‑mapping. U and V are the coordinates of the texture corresponding to X and Y. Think of u as one direction on a piece of graph paper (side to side). Think of v as the other direction (up and down).
Any time an image is applied in a material and then applied that material to a model, uv‑texture mapping is used.
Mapping channel
A mapping channel holds a set of texture-mapping parameters. Each mapping channel is identified by a number. An object can have any number of channels and therefore can hold any number of texture mapping types.
Textures in materials can be assigned a channel number. When the textures are applied to an object, the texture is applied using the matching channel number on the object. Texture channels default to channel 1.
If an object has no applied texture mapping, surface mapping is used to map the texture.
![]() Properties Panel
Properties Panel
Environment map, Screen, and WCS* mapping styles set in the material texture override texture mapping properties. You will see this message when it happens.
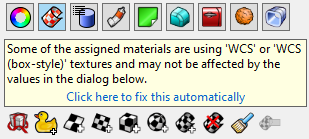
Click the blue text string below the message to change the material texture to use a mapping channel. Texture mapping properties will then take over the control.
 Unwrap
Unwrap
Unwraps the texture for editing.
See: Unwrap.
 Custom Mapping
Custom Mapping
Add a custom mapping channel.
 Surface Mapping
Surface Mapping
Add a surface mapping channel. The default texture mapping method for surfaces and polysurfaces is set by the control point structure of the surfaces.
 Planar Mapping
Planar Mapping
Add a planar mapping channel.
 Box Mapping
Box Mapping
Add a box mapping channel.
 Spherical Mapping
Spherical Mapping
Add a spherical mapping channel.
 Cylindrical Mapping
Cylindrical Mapping
Add a cylindrical mapping channel.
 Apply OCS Mapping
Apply OCS Mapping
Line up textures with the object rather than the world coordinates. Details...
 Delete Mapping
Delete Mapping
Delete a mapping channel.
 Match Mapping
Match Mapping
Match the mapping to another object's mapping.
 Edit Channel (Use multiple mapping channels only)
Edit Channel (Use multiple mapping channels only)
Allows changing the channel number.

 Show Mapping
Show Mapping
Display the mapping widgets for the object.
 Hide Mapping
Hide Mapping
Hide the mapping widgets for all objects.
 Select Mapping Widgets
Select Mapping Widgets
Select all texture mapping widgets of the selected object.
Use Show Mapping first.
 UVEditor
UVEditor
Opens the UV Editor.
See: UVEditor.
Use multiple mapping channels
Allows more than one mapping channel for a single object. The channel numbers can be changed by using the edit channel icon. These mapping channel numbers are used in the texture map settings for an objects material to control which mapping channel is used for that texture.
Channels
#
The mapping channel number.
Type
The mapping type.
Name
The name of the mapping.
Name
The name of the mapping.
See: Naming conventions in Rhino
Projection
Closest point
Ray
Type
The mapping type.
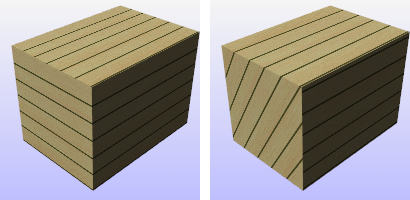
Surface
Surface mapping stretches the texture over the object.
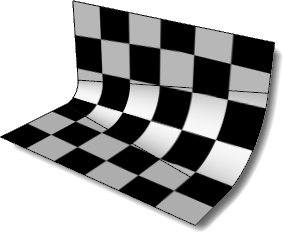
In this example, a variable radius fillet connects two planar surfaces and all are joined into one polysurface. The default surface mapping method uses the control point structure of each individual surface to orient the checkered texture map applied to the material. Notice how the checker texture does not match across seams in the polysurface.
See: ApplySurfaceMapping.

Planar
Planar mapping projects a 2-D plane onto the side of an object.
See: ApplyPlanarMapping.

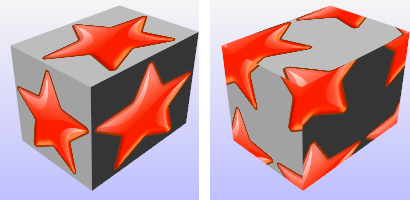
Box
Box mapping projects a 3-D box onto the sides and top of an object.
See: ApplyBoxMapping.

Box (sides only)
Box mapping sides of an object only, does not cap the mapping to the top and bottom surfaces.
See: ApplyBoxMapping.

Spherical
Spherical mapping wraps the object around a sphere. The top edge of the texture shrinks into the top pole and the bottom edge into the bottom pole.
See: ApplySphericalMapping.

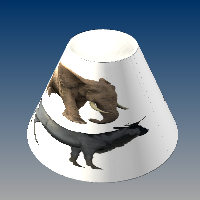
Cylindrical
Cylindrical mapping an image around an object like a cylinder the left and right edge will join each other.
See: ApplyCylindricalMapping.
Capped cylindrical
Capped cylindrical mapping also maps the image to the top and bottom of the objects.
See: ApplyCylindricalMapping.

OCS frame
The OCS frame type lines up textures with the object rather than the world coordinates when textures use WCS/OCS or WCS/OCS (Box style) mappings. This mapping type can only be added by the ApplyOcsMapping command.
Custom
Add a custom mapping channel.
Custom surface objects control the mapping of textures over any other object.
This process is limited to single surfaces as the surface control point structure is used to control the applied mapping. Here, the surface in front of the polysurface was selected when prompted for the custom object in the command line.
Custom Mapping Steps
- Select the custom mapping object.
Projection
When a mesh is texture mapped, some UV(W) values have to be assigned to each vertex from another object – either a primitive like a sphere or a custom object like another mesh or surface.
Each mesh vertex is assigned a parameter from the other object’s UV space.
Closest point
Finds the closest point on the primitive from the point on the mesh.
Ray
Ray draws a line from the mesh along its normal until it hits the primitive.
Texture space
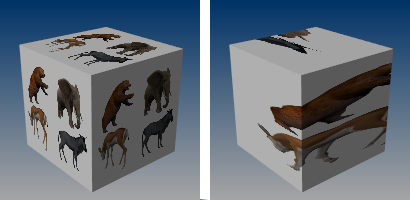
Single texture space (left), divided texture space (right).
Single
Specifies that the texture will be mapped individually over each independent space.
Divided
Specifies that distinct regions of the texture will be used for each space, matching parts of the mapped object to the six independent texture spaces.
XYZ position
Sets the center point of the texture mapping widget in world coordinates.
-
Right-click on the slider to set min/max value, incremental precision and decimal places for the value. They are used when you double-click on the slider to enter the value or use the up or down key to change the value.

Default position (left), position moved to a different location (right).
 Pick button
Pick button
Click to pick a location on the screen.
XYZ rotation
Sets the rotation of the texture in world space.
-
Right-click on the dial indicator to set incremental precision and decimal places for the angle value. They are used when you double-click on the dial indicator to enter the value or use the up or down key to change the value.

Default rotation (left), x rotation 60 degrees (right).
XYZ size
The texture size.
 Set size to one in all directions
Set size to one in all directions
Sets the texture size to 1 in all three directions.
 Set size to equal in all directions
Set size to equal in all directions
Sets the texture size to be equal in all three directions.
 Fit to object by original mapping
Fit to object by original mapping
Fits the texture to the object as established by the original mapping.
 Set size to aspect ratio of image
Set size to aspect ratio of image
Sets the size to the aspect ratio of the image.
 Lock Size
Lock Size
When the mapping widget has been re-sized with unequal scaling, the scaling is locked to the specified aspect ratio.
UVW offset
The amount the texture is offset from the origin of the UVW texture space.
UVW repeat
The number of times the texture repeats across the object in UVW texture space.
Lock
When Lock is checked, the repeat values for u, v, and w change together so that they stay in the same relationship to each other.
When Lock is unchecked, the repeat values can be changed independently of each other.
Example:
If Lock is off, and you enter 1, 2, 3 in the UVW boxes, you will get one repeat in u, two repeats in v, and three repeats in w.
If you then check Lock, and change the 1 to a 2, the values will change to 2, 4, 6. If you then change the 6 to 60, you will get 20, 40, 60.
UVW rotation
The rotation angle of the texture over the object in UVW texture space.
Related commands
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The ApplyBoxMapping command adds a box texture mapping channel to an object and sets the mapping type to box.
Object with box mapping widget on.
Steps
-
Select objects, and press Enter.
-
Draw the mapping widget box.
-
Select the coordinate system.
-
Specify if the box will be capped.
-
Enter a mapping channel number, or press Enter to accept the default value.
Command-line options
BoundingBox
Uses the object bounding box to determine the location and size of the mapping widget.
CPlane
Uses Construction plane coordinates for the bounding box.
World
Uses World coordinates for the bounding box.
Diagonal
Creates a box from the diagonal corners. If you pick the two corners on the CPlane, the command prompts for picking the height.

(Default)
Draws the rectangle using two opposite corners.
3Point
Draws the rectangle using two adjacent corner locations and a location on the opposite side.
EdgeMidpoint
Draws the rectangle from the midpoint of the first edge, an end of the edge, and a location on the opposite side.
Vertical
Draws the rectangle perpendicular to the construction plane.
Center
Draws the rectangle from the center point and a corner.
Capped
Applies the mapping to all six sides of the box.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The ApplyCylindricalMapping command adds a texture mapping channel to an object and sets the mapping type to cylindrical.

Surface mapping (left), cylindrical mapping (right).
Steps
-
Select objects, and press Enter.
-
Draw the mapping widget cylinder.
-
Select the coordinate system.
-
Specify if the cylinder will be capped.
-
Enter a mapping channel number, or press Enter to accept the default value.
Command-line options
BoundingBox
Uses the object bounding box to determine the location and size of the mapping widget.
CPlane
Uses Construction plane coordinates for the bounding box.
World
Uses World coordinates for the bounding box.
DirectionConstraint
Direction constraints restrict the direction of the cylinder.
None
Pick or type a number to set the height.

- Use elevator mode, object snaps, or other modeling aids to help picking a location.
- The cursor location defines the positive direction when you type a number to set the height.
Vertical
Creates a cylinder perpendicular to the construction plane.
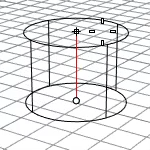
- The CPlane +Z direction defines the positive direction when you type a number to set the height.
AroundCurve
Draws the base circle perpendicular to the picked point on a curve. The center line of the cylinder will be tangent to the curve.
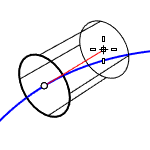
- The curve direction defines the positive direction when you type a number to set the height.
Radius
Draws the base circle by picking the center point and a radius point.
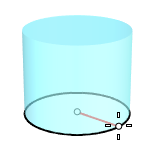
2Point
Draws the base circle from two opposite points.

3Point
Draws the base circle through three points.
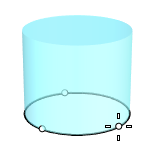
Tangent
Draws the base circle tangent to one, two, or three curves.

FitPoints
Draws the base circle by fitting to selected points, control points, or mesh vertices.
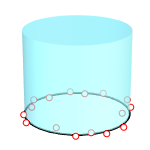
Capped
Applies the mapping to the top and bottom of the cylinder.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The ApplyCustomMapping command adds a custom texture mapping channel to an object.
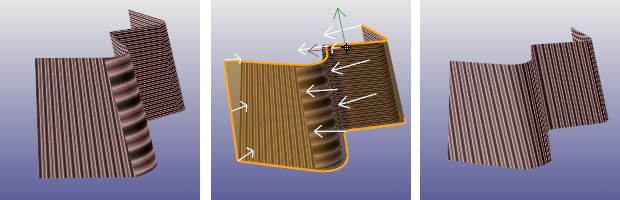
No mapping or surface mapping (left), custom mapping object (center), result of custom mapping.
A specified mesh or NURBS surface or polysurface acts as the mapping for the selected objects. The mapping object is preserved in the mapping table so deleting the mapping object does not affect the mapping on the target object.
Steps
- Select target objects.
- Select the custom mapping surface or mesh.
- Enter a mapping channel number, or press Enter to accept the default value.
-
The custom mapping object applied to objects can be extracted by the ExtractCustomMappingObject command.
|
Toolbar |
Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The ApplyOcsMapping command lines up textures with the object rather than the world coordinates when textures use WCS/OCS or WCS/OCS (Box style) mappings.
Steps
-
Select an object.
-
Specify the origin, X and Y directions to set the OCS mapping frame.
An OCS frame mapping type is added to the object's Texture Mapping properties.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The ApplyPlanarMapping command adds a texture mapping channel to an object and sets the mapping type to planar.
Steps
-
Select objects, and press Enter.
-
Draw the mapping widget box.
-
Select UV for 2D mapping, or UVW for 3D.
-
Enter a mapping channel number, or press Enter to accept the default value.
Command-line options
BoundingBox
Uses the object bounding box to determine the location and size of the mapping widget.
CPlane
Uses Construction plane coordinates for the bounding box.
World
Uses World coordinates for the bounding box.
Box
Draws a box to add a planar mapping widget.
(Default)
Draws the rectangle using two opposite corners.

3Point
Draws the rectangle using two adjacent corner locations and a location on the opposite side.

EdgeMidpoint
Draws the rectangle from the midpoint of the first edge, an end of the edge, and a location on the opposite side.

Vertical
Draws the rectangle perpendicular to the construction plane.

Center
Draws the rectangle from the center point and a corner.

AroundCurve
Draws a rectangle perpendicular to a curve.
UV
The U and V coordinates are taken from the plane size, the W coordinate is always zero.
UVW
The U and V coordinates are taken from the plane size, and the W coordinate is taken as the distance from the plane along the normal.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The ApplySphericalMapping command adds a texture mapping channel to an object and sets the mapping type to spherical.
Steps
- Select objects, and press Enter.
- Draw the mapping widget sphere.
- Enter a mapping channel number, or press Enter to accept the default value.
Command-line options
BoundingBox
Uses the object bounding box to determine the location and size of the mapping widget.
CPlane
Uses Construction plane coordinates for the bounding box.
World
Uses World coordinates for the bounding box.
Radius
Creates a sphere by picking the center point and a radius point.
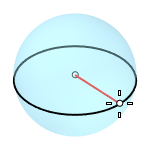
2Point
Creates a sphere from two opposite points on the base circle.

3Point
Creates a sphere from three points on the base circle.
Tangent
Creates a sphere with the base circle tangent to one, two or three curves.

AroundCurve
Creates a sphere from its center point on a curve, and a point on the base circle perpendicular to the curve.
4Point
Creates a sphere from three points on a section circle and a point on the sphere.

FitPoints
Creates a sphere by fitting to selected point objects, curve and surface control points, and mesh vertices.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The ApplySurfaceMapping command adds a texture mapping channel to an object and sets the mapping type to surface.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The ExtractUVMesh command creates separate mesh objects extracted from the flattened UV space meshes of a model.

Steps
- Select a supported object type.
- Specify a mapping channel.
- Draw a rectangle.
Command-line options
1to1
Creates the mesh with the approximate area of the 3-D object.
The mesh can be used by a cutting machine for cutting shapes out of a material.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The MappingWidget command turns on the mapping widgets for the selected objects.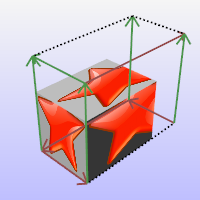
The box mapping widget:
- Shows graphically how the texture mapping is bound to an object using a primitive (box, cylinder, sphere, or plane).
- Can be dragged, moved, rotated, and scaled by normal Rhino commands.
- Can have its control points turned on to re-size it.
Command-line options
ShowOCSFrame
Displays the Object Coordinate System frame added to the object by the ApplyOcsMapping command.
This option is only visible when the selected object has an OCS frame.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The MappingWidgetOff command turns off the mapping widgets for selected objects.
Press to turn off all mapping widgets.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The MatchMapping command changes the texture mapping properties of a selected object to duplicate a specified object.
You can also use the Match Mapping button in Texture Mapping Properties.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The RemoveMappingChannel command removes the specified mapping channels from an object.
Steps
- Select objects.
- Type the mapping channel number.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The Unwrap command prompts for selecting edges on the selected object as texture seams where the object's render mesh will be split in UV space.
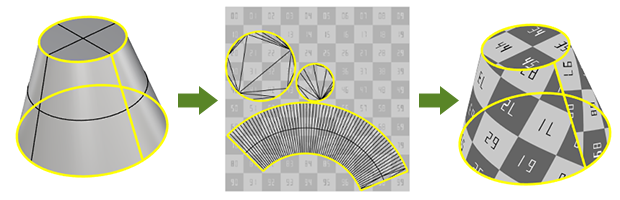
Input
- Surface, Polysurface, Extrusion, Mesh, SubD
Steps
-
Start the command.
-
Select one or multiple objects, press .
Multiple selected objects will not overlap in UV space.
-
Select a mapping channel.
-
Select edges on the object.
Use the command-line options to help selecting edges.
-
Press when done.
- Use the UVEditor command to edit the flatten render mesh in UV space to specify which portion of the material texture will display on the object.
- Use the same steps to add/remove unwrap seams of an object.
Command-line options
Chain
Chain selects the seams.
Apply
Applies the seam selection.
Edit
Opens the UV Editor.
Cancel
Cancels the command.
MappingChannel
Selects a mapping channel number for the UV mesh.
UnweldedOnly (For mesh-only)
Makes only unwelded mesh edges selectable.
SymmetryTip
Defines the symmetrical plane on an object to unwrap the object symmetrically.

See the Rectangle command for sub-option descriptions.
UnweldSeams (Mesh-only)
Unwelds the mesh edges along the seams to avoid mapping distortion near the seams. The actual mesh geometry will be modified.
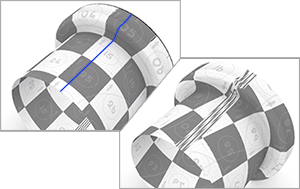
Method
Conformal
Uses the Least Squares Conformal Map (LSCM) algorithm to flatten 3D objects.
AngleBased
Uses the Angle Based Flattening (ABF++) algorithm to flatten 3D objects.
-
ABF (left) gives a more symmetric result than LSCM (right).
-
ABF requires even mesh tessellation to produce better results. Disable Simple planes and set Maximum aspect ratio smaller than 2 in the document render mesh settings to create the kind of render meshes.
AsRigidAsPossible
Uses the As-Rigid-As-Possible (ARAP) algorithm to flatten 3D objects. ARAP keeps texture size more even across the object than LSCM and ABF.
ShowEnds
Displays points on the open ends of selected unwrap seams.
See Also
Materials and texture mapping in Rhino 6 for Windows
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The UVEditor command edits meshes that affect the texture coordinates of the original object. The texture meshes can be joined and split, and their control points edited.
Steps
- Select objects.
- Edit the UV mesh in the UVEditor window.
Scriptable command-line options
To access scriptable command-line options
- Type a hyphen in front of the command name: -UVEditor.
Mapping Channel
The UV mesh of the specified channel displays when UV Editor opens. More information...
-
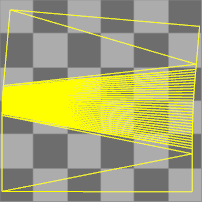
The packed surface mapping texture coordinates are projected onto the world xy plane, and the texture assigned to the object is drawn in the same region.
-
The texture coordinates are represented as a collection of UV meshes.
-
When the UV meshes are edited, the texture changes on the object.
-
If an interior surface seam is selected in the polysurface when unwrapping, that seam will separate in the resulting flattened mapping meshes.
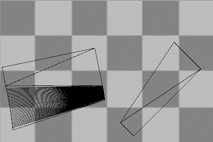
-
While the editor is open, vertices of the UV mesh can be turned on, and editing commands such as Scale1D, SetPt, and CageEdit can be used to adjust the UV mesh.
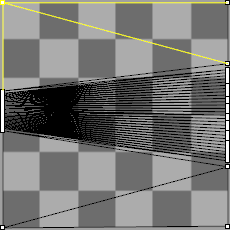
-
Meshes without UV coordinates (e.g., imported from STL files) do not have UV meshes to edit. You will need to unwrap the mesh, or apply a texture mapping to the mesh, before using the UVEditor command.
UV Islands
A UV island is an independent part of a UV mesh.
From mapping channel
Select a mapping channel to display the associated UV mesh in the view.
 Hide unused UV islands
Hide unused UV islands
Hides the UV islands that do not have textures assigned.
Mesh color
The color for the UV meshes with textures assigned.
Unused color
The color for the UV meshes without textures assigned.
 Show on model
Show on model
Controls whether to show the UV texture mesh wires on the 3-D object in model viewports.
 Pack texture meshes
Pack texture meshes
Fits all the UV meshes visible in the UV Editor into the unit domain (0,1)x(0,1) without overlaps. All meshes are uniformly scaled with the same factor. The packed meshes can be rotated and moved individually.
 Selection from model
Selection from model
Selects the UV mesh faces which are currently selected on the 3-D model.
Unwrapping
 Add vertex pinning constraint
Add vertex pinning constraint
Locks selected vertices in place while the UV mesh adjust to accommodate new constraints.
 Add edge straightening constraint
Add edge straightening constraint
Makes the selected edge chain as straight as possible while the UV mesh adjust to accommodate new constraints.
 Constrain edges to curve
Constrain edges to curve
Aligns selected edges to follow a specified curve. This constraint ensures the edges adapt to the curve's shape during UV adjustments of new constraints.
 Remove constraints
Remove constraints
Removes all types of constraints from selected UV islands.
Unwrap method
Select the unwrap method for re-unwrapping.
Each UV island can be unwrapped using a different method.
Conformal
Uses the Least Squares Conformal Map (LSCM) algorithm to flatten 3D objects.
AngleBased
Uses the Angle Based Flattening (ABF++) algorithm to flatten 3D objects.
-
ABF (left) gives a more symmetric result than LSCM (right).

-
ABF requires even mesh tessellation to produce better results. Disable Simple planes and set Maximum aspect ratio smaller than 2 in the document render mesh settings to create the kind of render meshes.
AsRigidAsPossible
Uses the As-Rigid-As-Possible (ARAP) algorithm to flatten 3D objects. ARAP keeps texture size more even across the object than LSCM and ABF.
 Re-unwrap selected
Re-unwrap selected
Re-unwraps the selected UV meshes manually.
 Automatic
Automatic
Controls whether the UV meshes are automatically re-unwrapped when modifying constraints.
Notes
- When a constraint point leaves the UV mesh, a green line appears between the constraint point and the corresponding UV mesh vertex.
- Constraint points and edges move with the parent UV island.
Viewport
 Reset zoom
Reset zoom
Fits the UV space rectangle to the view.
 Capture to clipboard
Capture to clipboard
Copies the UV space rectangle as an image of 1024x1024 pixels to the clipboard. You can then paste the image in other applications as a reference for painting the texture.
 Save to bitmap
Save to bitmap
Saves the UV space rectangle as an image of 1024x1024 pixels in one of the formats: *.jpg, *.png, *.bmp, *.tiff, and *.tga.
Texture transparency
Sets visibility level of the texture in the UVEditor window.
- Move the slider, or double-click the slider to enter the transparency value.
 Highlight selected
Highlight selected
Controls whether to highlight selected UV islands on the 3-D object in model viewports.
 Show wireframe
Show wireframe
Shows the object mesh in model viewports.
Texture
 Use material
Use material
Displays the texture of the material assigned to the object.
List of textures
Select the texture to show in the UV space view if the material uses multiple textures.
 Use texture
Use texture
Displays a specified texture from the Textures panel.
See also
Render
Render the objects using the current renderer.
Materials and texture mapping in Rhino 6 for Windows
About.com: Surfacing 101 - Texture Mapping
|
Toolbar |
Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The ExtractCustomMappingObject command extracts the custom mapping source, a mesh or a surface, embedded in the selected object.
|
Toolbar |
Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
The SetMeshSurfaceParameters command bakes the custom mapping of a mesh object into its default surface mapping.
This is useful as a pre-step for commands (e.g., Squish) that modify meshes but do not update the texture mapping.
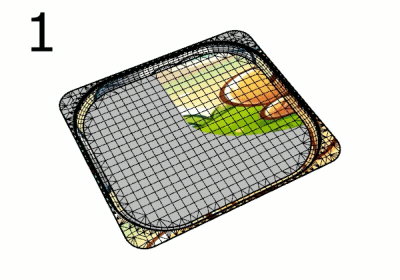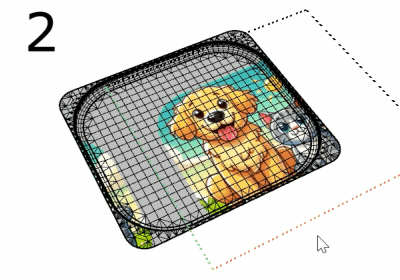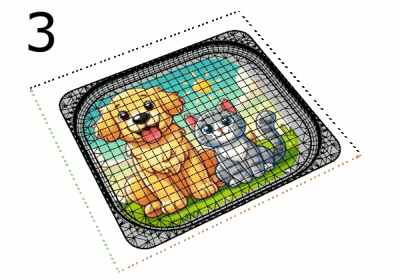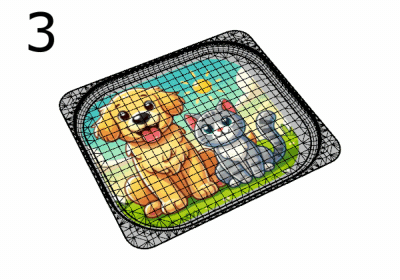
Steps
-
Select a mesh with a custom mapping applied to a channel.
-
Select that mapping channel.
-
Delete the mapping channel.
The mesh then uses its default surface mapping, and the texture appears the same as if the custom mapping were used.

