Dimension commands
Dimension commands create dimensions that annotate length, angle, radius, etc. parallel to the active CPlane. Dimensions are attached to the object by History.
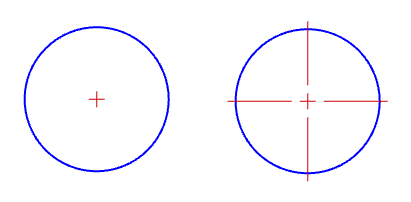
The Centermark command draws a cross or a cross and center lines at the center point of a curve.
The size and style of the centermark are controlled by the Annotation style and the Centermark properties.
- Dimensions have History recorded by default. The default History recording behavior is controlled by the RecordAnnotationHistory option in the History command.
Centermark style
Sets the style of the centermark for radius and diameter dimensions
None
No centermark is drawn.
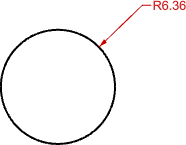
Mark
A cross mark is drawn at the center of the radius or diameter.

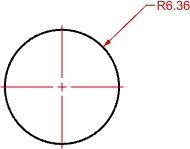
Mark and Lines
A cross mark and lines that extend to just beyond the edges of the object.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Dimension Linear Dimension |
The Dim command draws horizontal or vertical linear dimensions.
Steps
- Start the command.
- Pick two points.
-
Pick the third point to locate the dimension line.
When the dimension text does not fit between the extension lines, you can place the dimension text on left or right.
- Dimensions have History recorded by default. The default History recording behavior is controlled by the RecordAnnotationHistory option in the History command.
- Linear dimension line and text stick to their locations when the object is moved. If you need to relocate the linear dimension line and text with the object, they have to be moved together.
| Command-line options | |
|---|---|
|
Style |
Select the annotation style name. |
|
Object |
Select an object to dimension. |
|
Add more (chain) dimensions along the same dimension line. |
|
|
Undo |
Reverses the last action. |
|
Baseline |
Continues dimensioning from the first point.
|
|
Draws the dimension aligned with the construction plane y axis. |
|
|
Draws the dimension aligned with the construction plane x axis. |
|
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Dimension Aligned Dimension |
The DimAligned command draws a linear dimension lined up with two points.
Steps
- Start the command.
- Pick two points.
-
Pick the third point to locate the dimension line.
When the dimension text does not fit between the extension lines, you can place the dimension text on left or right.
- Dimensions have History recorded by default. The default History recording behavior is controlled by the RecordAnnotationHistory option in the History command.
- Linear dimension line and text stick to their locations when the object is moved. If you need to relocate the linear dimension line and text with the object, they have to be moved together.
| Command-line options | |
|---|---|
|
Style |
Select the annotation style name. |
|
Object |
Select an object to dimension. |
|
Continue |
Add more (chain) dimensions along the same dimension line. |
|
Baseline |
Continues dimensioning from the first point.
|
|
Undo |
Reverses the last action. |
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Dimension Angle Dimension |
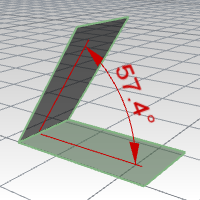
The DimAngle command dimensions the angle of an arc, or between two selected lines, or from three points.
Steps
- Dimensions have History recorded by default. The default History recording behavior is controlled by the RecordAnnotationHistory option in the History command.
| Command-line options | |
|---|---|
|
Style |
Select the annotation style name. |
|
Points |
Pick the apex of the angle (1) and then the dimension points (2) and (3). |
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Dimension Area Dimension |
The DimArea command dimensions the area of closed planar curves, surfaces, polysurfaces, sub-surfaces, meshes, or hatches.
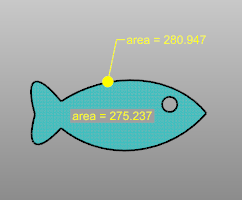
Steps
- Dimensions have History recorded by default. The default History recording behavior is controlled by the RecordAnnotationHistory option in the History command.
| Command-line option | |
|---|---|
|
Style |
LeaderUses a leader to point to the object. TextPlaces the text at the picked location. The dimension uses the Area text field for calculating the dimension. |
To edit existing dimensions
- Select the dimension, and edit the leader or text in the Properties panel.
- Or, double-click the dimension to open the leader or text edit box.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Dimension Curve Length Dimension |
The DimCurveLength command dimensions the length of a curve.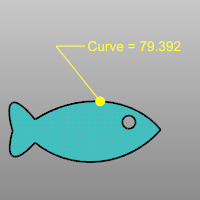
Steps
- Dimensions have History recorded by default. The default History recording behavior is controlled by the RecordAnnotationHistory option in the History command.
| Command-line option | |
|---|---|
|
Style |
LeaderUses a leader to point to the object. TextPlaces the text at the picked location. The dimension uses the CurveLength text field for calculating the dimension. |
To edit existing dimensions
- Select the dimension, and edit the leader or text in the Properties panel.
- Or, double-click the dimension to open the leader or text edit box.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Dimension Crease Angle Dimension |
The DimCreaseAngle command dimensions the angle between two planes.
- Dimensions have History recorded by default. The default History recording behavior is controlled by the RecordAnnotationHistory option in the History command.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
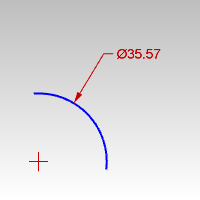
Dimension Diameter Dimension |
The DimDiameter command dimensions the diameter of a selected curve.
Steps
- Dimensions have History recorded by default. The default History recording behavior is controlled by the RecordAnnotationHistory option in the History command.
| Command-line option | |
|---|---|
|
Style |
Select the annotation style name. |
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Dimension Ordinate Dimension |
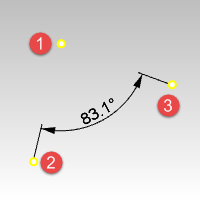
The DimOrdinate command dimensions the x or y distance from a base location.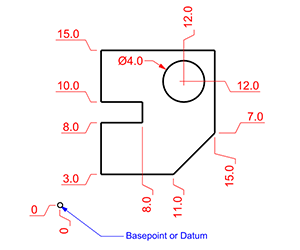
Note
- Ordinate dimensions show the horizontal or vertical distance from an origin point (called the basepoint) to a dimensioned feature, such as a hole Center or a feature in a part.
- The DimOrdinate command annotates the absolute distance in the X or Y axis between two points. It is always positive and different from vectors that may be negative.
- Ordinate dimensions are widely used in CNC related manufacturing industries because the clutter caused by dimensions is minimized.
- This type of dimension prevents accumulated errors by showing the X or Y offset of the feature from the basepoint.
-
The shape of the ordinate leader can be point edited after creation to avoid overlapping geometry.
Create an Ordinate dimension
Update an Ordinate dimension
- Select an Ordinate dimension.
- Turn on its control points. (Edit > Control Points > Control Points On)
- Move the base point (1) or dimension point (2) to a new location.
Dimension text (3) will update if History was recorded.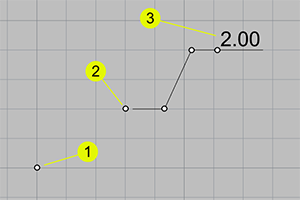
- Dimensions have History recorded by default. The default History recording behavior is controlled by the RecordAnnotationHistory option in the History command.
| Command-line options | |
|---|---|
|
AnnotationStyle |
Select the annotation style name. |
|
XDatum |
Overrides the implied biasing and forces an X ordinate dimension. |
|
YDatum |
Overrides the implied biasing and forces a Y ordinate dimension. |
|
Basepoint |
Changes the basepoint for the duration of the command. The basepoint reverts to the default construction plane origin when the DimOrdinate command is run again. |
| KinkOffset |
Decides the offset distance of the two kinks (1) (2) before the leader endpoint (3). This option appears after the first point is picked. 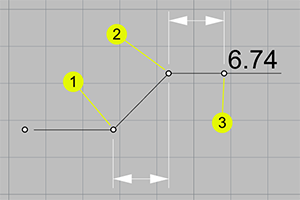
|
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
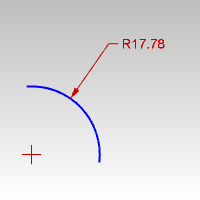
Dimension Radial Dimension |
The DimRadius command dimensions the radius of an arc or circle.
Dimensions always measure as though the object were projected to the current construction plane.
- Dimensions have History recorded by default. The default History recording behavior is controlled by the RecordAnnotationHistory option in the History command.
| Command-line options | |
|---|---|
|
Style |
Select the annotation style name. |
|
PointOnCurve |
Pick a point on the curve where the dimension arrow will start. |
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Dimension Rotated Dimension |
The DimRotated command draws a linear dimension that is rotated from the xy axis.
Steps
- Start the command.
- Enter a number to set the rotation angle of the dimension line.
The rotation angle can also be set by picking two points. - Pick two points.
- Pick the third point to locate the dimension line.
When the dimension text does not fit between the extension lines, you can place the dimension text on the left or right side.
- Dimensions have History recorded by default. The default History recording behavior is controlled by the RecordAnnotationHistory option in the History command.
- Linear dimension line and text stick to their locations when the object is moved. If you need to relocate the linear dimension line and text with the object, they have to be moved together.
| Command-line options | |
|---|---|
|
Style |
Select the annotation style name. |
|
Object |
Select an object to dimension. |
|
Continue |
Add more (chain) dimensions along the same dimension line. |
|
Baseline |
Continues dimensioning from the first point.
|
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Dimension Recenter Dimension Text |
The DimRecenterText command returns dimension text to its default location.
Steps
- Select dimensions.
To move dimension text away from the dimension line, turn on the dimension control points and drag the text control point.
Text
Style
The used annotation style.
Style menu
Lists the annotation styles available in the model. If an annotation has any settings in its properties different from its style, a menu behind the style name appears.
Remove overrides
Resets all the changed settings to the style defaults.
Update <Style> to match
Applies the changed settings to the annotation style.
Save as new style
Uses the settings in the properties to create a new style.
Edit Style...
Edits the Annotations style used by the selected annotation object.
Height
The text height.
Mask
Surrounds text with an opaque color.
None
Turn off mask.
Background
Sets the mask color to the viewport background color.

Solid Color
Selects the mask color using the Select Color dialog box.
Mask Color
When Mask is set to Solid Color, click to change the color.
Mask margins
The width of the blank area around the text.

Model space scale
The display size is a product of the component's size (like arrow size or text height) and the Model space scale value.
Normally this is the inverse of the print scale. The text height, extension line extension, extension line offset distance, and arrow length are multiplied by this number.
 Draw frame around text
Draw frame around text
Displays a rectangle enclosing the text in annotations. The Mask margins setting controls the distance between the text and rectangle.

Font
The text appearance.
-
Click to open the drop-down list, and type the initial letter of a font to find the font quickly.
-
Click the font control and scroll the mouse wheel through the list to select a font.
-
If a font used by an annotation is missing on the current system:
You will be prompted when the model is opened.

Enable the "Don't show this message again" checkbox in the warning dialog box to stop detecting missing fonts.
To re-enable missing font detection, enable Rhino.Warnings.MissingFontWarning in Rhino Preferences > Advanced.
The annotation displays with a substitute font in viewports.
The missing font is listed with "(not installed)" in the font list.
B
Sets the font style to bold.
I
Sets the font style to italic.
U
Sets the font style to underlined.
 Text Field
Text Field
Text fields are formulas that are evaluated while Rhino is running and the result is displayed in the text. All text fields are in the syntax of %<field and options>%. When a formula cannot be evaluated an error string of #### is displayed.
- If a text field displays a long text string, such as a long file path, you can turn on control points of the text and move the right text point to wrap the text string.

- Text fields support basic arithmetic operations.

To double an area, add *2 behind the close parenthesis as:
%<Area("d90815b8...80c59a")*2>%
To multiply two text fields, use:
%<CurveLength("07c73fde...8a5c7b")*CurveLength("296ed593...0472e0")>%
 Toggle stacking brackets
Toggle stacking brackets
The toggle stacking brackets button is a shortcut to add or remove [[...]] around text selected in the edit box. Stacking brackets will make the text between them stack, so that [[1/2]] will display as a stacked fraction.
 Degree
Degree
Enters a degree symbol (°) into the text.
 Radius
Radius
Enters a radius symbol (R) into the text.
 Diameter
Diameter
Enters a diameter symbol (Ø) into the text.
 Plus/Minus
Plus/Minus
Enters a plus/minus symbol (±) into the text.
 Exponent 2
Exponent 2
Enters a superscript 2 (²) into the text.
 Exponent 3
Exponent 3
Enters a superscript 3 (³) into the text.
Edit Box
Angle brackets
The angle brackets < > represent the dimension value. You can type additional text before or after the angle brackets, or you can eliminate the angle brackets.
To type multi-line text, press and hold Alt and press Enter.
Dimension display
The current dimension value.
Font size of the edit box can be controlled by command prompt options.
Edits the Annotations style used by the selected annotation object.
Select an annotation to apply its properties to the current annotation.
Fit text
Auto
Automatically determines where to place the text.
Inside
Forces the text to the inside of the dimension lines.

Right
Forces the text to the outside and to the right of the dimension lines.

Left
Forces the text to the outside and to the left of the dimension lines.
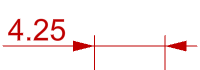
HintLeft/HintRight
HintLeft and HintRight are automatically selected based on where you pick to place the dimension line. Picking on the left, HintLeft is selected. Picking on the right, HintRight is selected. When the dimension is changed, and the dimension text no longer fits between the extension lines, the dimension text will be moved to the left or right side.
|
|
|
|
HintLeft
|
HintRight
|
Dimension lines
Arrows
Arrowhead 1 / 2
 Arrow
Arrow
 Dot
Dot
 Tick
Tick
 Short arrow
Short arrow
 Open arrow
Open arrow
 Rectangle
Rectangle
 Thin arrow
Thin arrow
 Thinner arrow
Thinner arrow
User arrow
Uses a previously defined block as an arrowhead.
This option is not available when no blocks exist in the model.
To create a block to represent the arrowhead
- Draw the arrow elements.
- Create a block from the geometry.
Note
-
The base point of the arrowhead block determines how the arrowhead is placed on the end of a dimension line or a leader. In the illustration below:
(1) The base point of the arrowhead block is placed at the tip of the arrowhead curve. The dimension line passes the arrowhead.
(2) The base point of the arrowhead block is placed at the end of the arrowhead curve. The dimension line does not pass the arrowhead.

If you want the tip of the arrowhead to be accurately placed at a location, be sure to place the base point of the arrowhead block at the tip.
- Make use of the By object, By layer, and By parent features of the Block command to control the appearance of the arrow.
No arrow
No arrow is drawn.

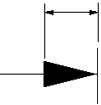
Arrow size
The length of the arrowhead from tip to tail.
Fit arrow
When there is not enough space for the arrows, you can force their position.
Auto
Automatically determines where to place the arrows.
Inside
Forces the arrows to the inside of the dimension lines.

Outside
Forces the arrows to the outside of the dimension lines.

Draw dimension line between extension lines if arrows are outside
Force drawing the dimension line when the arrows are on the outside.

Length units
Unit - Format
The unit and format of the annotation style.
Length factor
Distances in dimensions are multiplied by this value.
Linear resolution
The number of decimal places for the distance display.
Round off
Rounds off the dimension to the nearest listed value.
Prefix / Suffix
Text added before and after the dimension text.
Prefix and suffix only display when the dimension text string contains "<>".
Zero suppression
Turns off the display of zeros at the beginning or end of the dimension.
No zero suppression
0.560
Suppress leading zeros
.560
Suppress trailing zeros
0.56
Suppress leading and trailing zeros
.56
Alternate units
 Use alternate units
Use alternate units
Displays the second units in linear dimensions.
Unit - Format
The unit and format of the annotation style.
Length factor
Distances in dimensions are multiplied by this value.
Linear resolution
The number of decimal places for the distance display.
Round off
Rounds off the dimension to the nearest listed value.
Prefix / Suffix
Text added before and after the dimension text.
Prefix and suffix only display when the dimension text string contains "<>".
Zero suppression
Turns off the display of zeros at the beginning or end of the dimension.
No zero suppression
0.560
Suppress leading zeros
.560
Suppress trailing zeros
0.56
Suppress leading and trailing zeros
.56
 Alternate units below
Alternate units below
Displays alternate units on the other side of the dimensions lines.
Tolerance
Tolerance style
Controls how the tolerance is formatted or displayed on the dimension line.
No tolerance
No tolerance is added.
Symmetrical
Adds a ± (plus/minus) character and single Upper value.

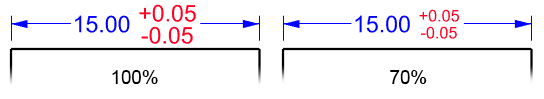
Deviation
Displays the Upper value preceded by a + (plus) character and the Lower value preceded by a - (minus) character on the dimension line. Entering a negative number reverses the tolerance display from positive to negative and negative to positive.

Limits
Displays the dimension length plus the Upper value and the dimension length minus the Lower value.

Resolution
Specifies the number of decimal places for the tolerance value.
Alt resolution
Specifies the number of decimal places for the tolerance value in the alternate units.
Upper value
Specifies the maximum or upper tolerance value.
Lower value
Specifies the minimum or lower tolerance value.
Text height scale (%)
Specifies the relative text height for the tolerance values. This setting is only for stacked types of tolerances.
More properties
See: Annotation: Arrows
See: Annotation: Leaders
|
Toolbar |
Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Dimension Set Dimension Layer |
The SetDimensionLayer command decides if dimensions will be created on the current layer or the specified layer.
-
The dimension commands affected:
Dim, DimAligned, DimAngle, DimCreaseAngle, DimDiameter, DimOrdinate, DimRadius, DimRotated
To set a dimension layer
-
Select Specify Layer.
-
Enter a layer name.
-
If the layer does not exist, the layer will be created.
-
The specified layer applies to every modeling window of the current Rhino application session.
-
Command-line options
UseDimensionLayer
UseCurrentLayer
Creates dimensions on the current layer.
SpecifyLayer
Creates dimensions on a specific layer.
DimensionLayerName
The name of the layer for creating dimensions.