ChamferSrf
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Surface Chamfer Surfaces |
The ChamferSrf command creates a ruled surface as a bevel between two input surface edges.
Steps
-
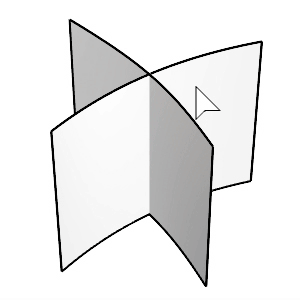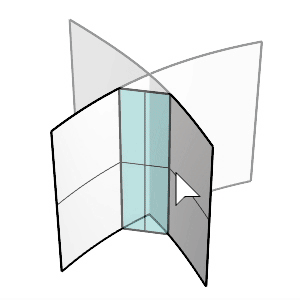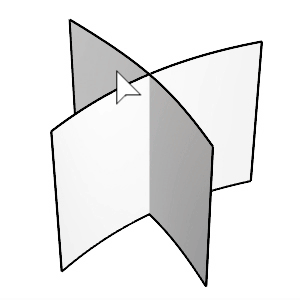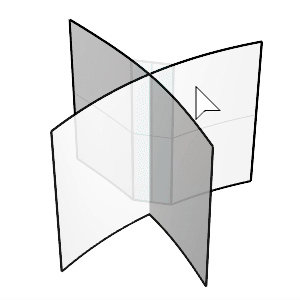
Select the first and second surfaces.
Click the surfaces on the side you want to keep after chamfering.
Warning
This command works on the analogy of rolling a ball of a defined radius along the edges of the surfaces. If a corner is narrower than the ball radius, the ball cannot negotiate the turn, which can cause the command to fail.
Command-line options
Distances
The distance from the intersection of the surfaces to the edge of the chamfer.
Extend
When one input surface is longer than the other, the chamfer surface is extended on the longer edge.
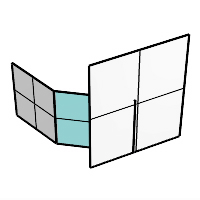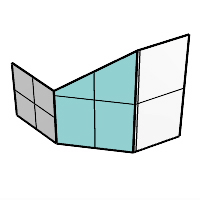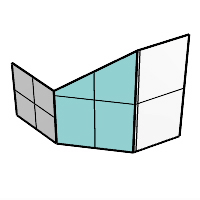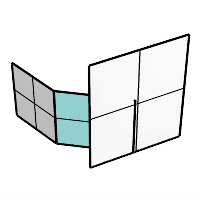
Trim
Trims the original surfaces to the intersections with the resulting surface.
History is supported when the Trim=No.
Split
Splits the original surfaces at the resulting surface edges.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Surface Fillet Surfaces |
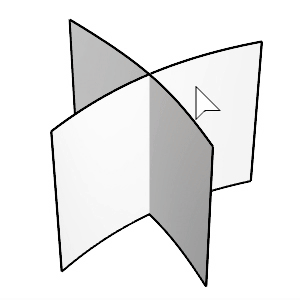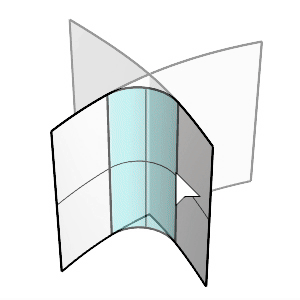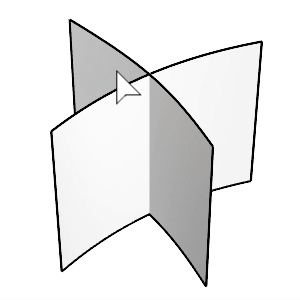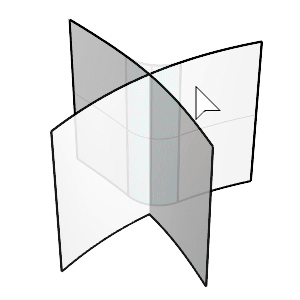
The FilletSrf command creates a constant-radius round surface between two surfaces.
Steps
-
Select the first and second surfaces.
Click the surfaces on the side you want to keep after filleting.
Warning
This command works on the analogy of rolling a ball of a defined radius along the edges of the surfaces. If a corner is narrower than the ball radius, the ball cannot negotiate the turn, which can cause the command to fail.
Tips
- Always fillet from the largest radius to the smallest radius across a model.
- Remove any edges you can prior to filleting with MergeAllCoplanarFaces or by way of surfacing in a simpler manner. Fewer intersected edges = Fewer problems as the fillet rolls along any edges and tries to trim and join with the adjacent surfaces.
- Make sure there is enough room for the fillet surface to trim and join with adjacent surfaces. The angle relationships between surfaces, sharpness of the bend in the rail around corners and rail type all play a part in any particular case.
Command-line options
Radius
Sets the radius of the fillet surface. It will be the initial value of the Radius slider in the options dialog
Options
Radius
Move the slider to change the radius, or double-click on the slider to enter a value.
Range
Click a number button to change the range of the slider for smaller or larger adjustment.
Blend Type
 Arc
Arc
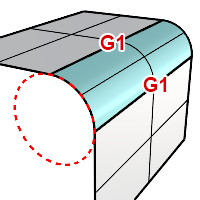
Creates a fillet surface with arc sections and tangent (G1) to the input surfaces.
 Deformable
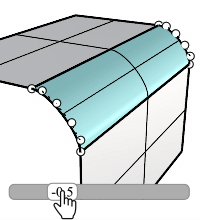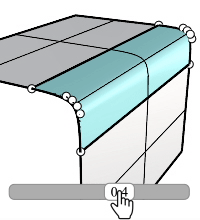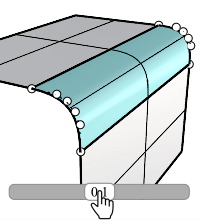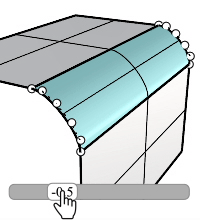
Deformable
Adds more control points to the fillet sections for adjusting tangency and bulge.
Deformable degree
Sets the degree of fillet sections from 3 to 5.
Tangent
Moves the second points on both ends in the tangent direction.
Bulge (For degree 4 and 5)
Moves the point(s) in the middle to make the fillet sections sharper or flatter.
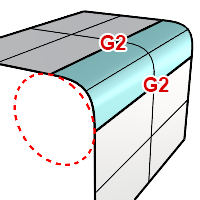
 G2 Blend
G2 Blend
Creates a blend surface connecting to the input surfaces with curvature (G2) continuity.
 Trim
Trim
Uses the output surface to trim the input surfaces when possible.
History is supported only when the Trim checkbox is disabled.
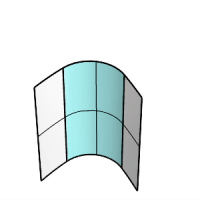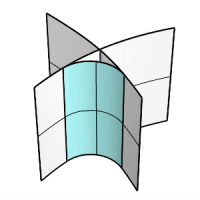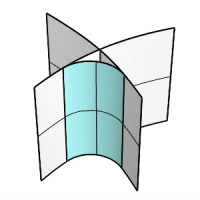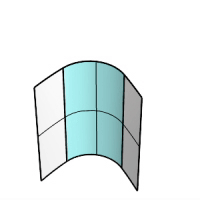
 Extend
Extend
If one input surface is longer than the other, the output surface is extended along the longer edge.