ArrayCrv
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Transform Array > Along Curve |
The ArrayCrv command copies objects spaced along a curve.
Steps
- Select objects to array.
- Select a path curve near the end where you want the array to start.
Or
Use the Basepoint option. - Specify the number of elements to array or the spacing distance along the curve.
- Type a value of 1 or more for the number of elements.
Command-line options
Basepoint
When the object to be arrayed is not on the curve and should be moved to the curve prior to the array, the Basepoint option establishes a reference location that will be move to the curve.
Items
The number of items array along the curve.
Distance
The distance between items. The number of items is determined by the length of the curve.
Orientation
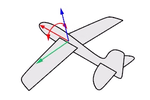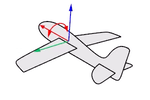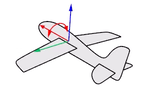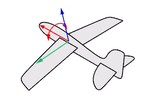
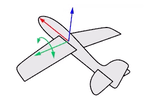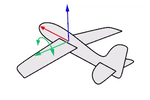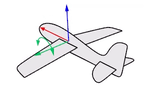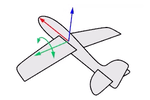
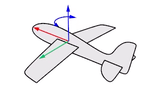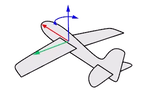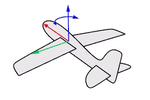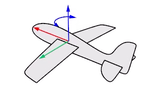
Think about an airplane. An airplane may Roll, Pitch, or Yaw when it flies in the air. The orientation styles control how the object rolls, pitches, or yaws when it arrays along a curve.
|
|
|
|
|
Roll rotates around the x-axis.
|
Pitch rotates around the y-axis.
|
Yaw rotates around the z-axis.
|
NoRotation
The object does not roll, pitch, or yaw. It is only copied to different locations on the curve.
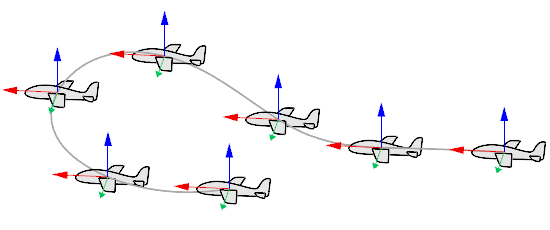
FreeFrom
The object rolls, pitches, and yaws at the same time along the curve.
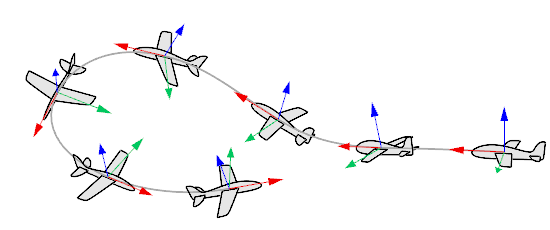
Roadlike
The object pitches and yaws but does not roll. The y-axis (green) is always parallel to the CPlane of the selected viewport.
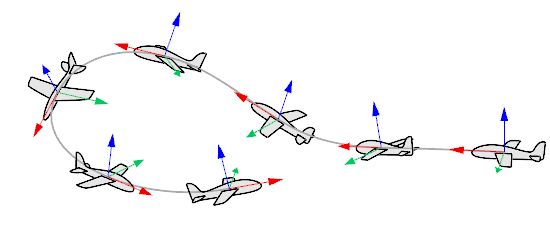
SubCrv
When selecting the path curve, type subcrv to select part of a curve.
| Toolbar | Menu |
|---|---|
|
|
Transform Array > Along Curve on Surface |
The ArrayCrvOnSrf command copies objects spaced and rotated along a curve on a surface.
Details
The surface normal determines the orientation of the arrayed objects.
Steps
| Command-line options | |
|---|---|
|
Divide |
Type the number of objects. |
|
Multiple |
Specify the distance between objects.
|
|
Type subcrv to select part of a curve as input. |
|