ExtractMeshEdges
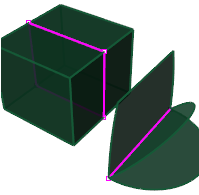
The ExtractMeshEdges command separates edges from the parent mesh determined by an angle between mesh face normals.
The command may help if you have a mesh that came from a polysurface but no longer have the polysurface. Using the command with the Unwelded option creates polyline approximations of where the edges of the polysurface were.
Notes
| ● | Some STL/SLA printers have problems if meshes contain many long, thin facets. These can slow the printer's slicing process down, produce odd printed results, and run the printer out of memory. |
| ● | The MeshRepair command may be useful when tuning up meshes for STL/SLA printing. |
Steps
Select a mesh.
Command-line options
Extract edges by
Unwelded
Extracts edges with coincident vertices.
Break angle
The angle between the face normals of adjacent faces.
Greater than
Specify a minimum break angle.
Select Edge
Specify an example edge to set the minimum break angle.
Less than
Specify a maximum break angle
Select Edge
Specify an example edge to set the maximum break angle.
Join results
Joins the resulting curves.